Living in an era where the consequences of climate instability are becoming increasingly evident, it is crucial for individuals, communities, and nations to take responsibility for their environmental impact.
One of the essential concepts in this regard is the carbon footprint. In this post, we breakdown the intricacies of carbon footprint, its significance, and ways to reduce it. By understanding and addressing our footprint, we can contribute to a more sustainable future.
The average carbon footprint per person varies across countries.
According to the World Bank, in the United States, the average per capita carbon footprint is approximately 16.2 metric tons of CO2 equivalent per year.
In comparison, the global average is about 4 metric tons per year.
What is Carbon Footprint?
Carbon footprint is the measure of greenhouse gas emissions, specifically carbon dioxide (CO2), associated with human activities. It represents the total amount of CO2 released directly or indirectly through activities such as transportation, energy consumption, manufacturing, and even food production.
Each individual, organization, or product has a carbon footprint, and it is typically measured in metric tons of CO2 equivalent per year.
The Significance of Carbon Footprint
Understanding our carbon footprint is essential because it allows us to comprehend the impact of our daily actions on the environment. By quantifying our emissions, we can identify the major sources and adopt measures to reduce them.
Carbon footprints also enable individuals, businesses, and governments to set targets, track progress, and implement sustainable practices effectively.
Furthermore, reducing carbon emissions can help mitigate climate instability, preserve natural resources, and enhance overall environmental sustainability.
Largest Sources of Global Greenhouse Carbon Emissions
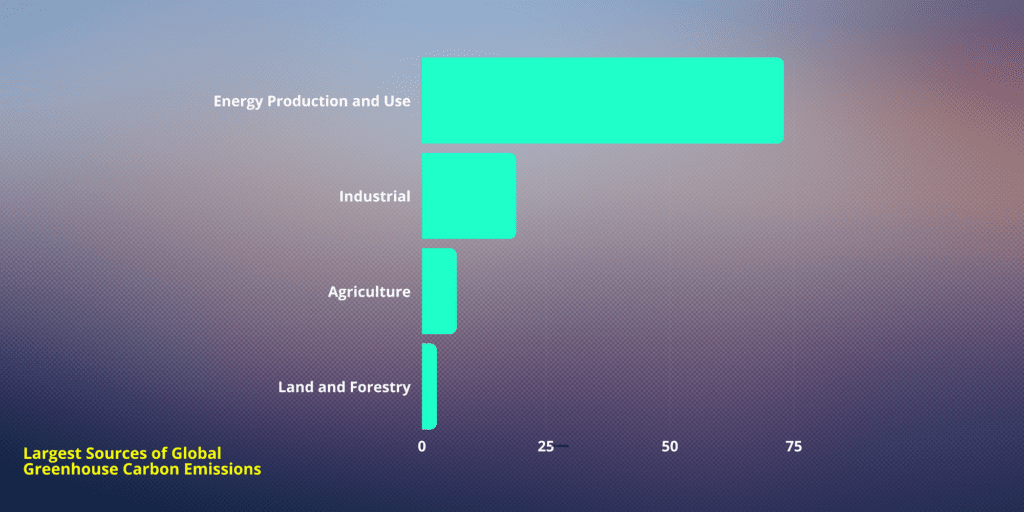
- Energy Production and Use: Energy production and consumption is the largest contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for approximately 73% of total emissions. This includes the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas for electricity generation, heating, and industrial processes.
- Industry: The industrial sector is responsible for about 19% of global greenhouse gas emissions. This includes emissions from manufacturing processes, chemical production, cement production, and the use of industrial gases such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and perfluorocarbons (PFCs).
- Agriculture: Agricultural activities contribute to approximately 7% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Emissions in this sector primarily arise from livestock production, rice cultivation, agricultural soil management, and the use of synthetic fertilizers. Livestock, especially ruminants like cattle and sheep, produce significant amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Land Use Changes and Forestry: Land use changes, such as deforestation, and forestry practices contribute to approximately 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Deforestation releases stored carbon into the atmosphere, while afforestation and reforestation projects can help absorb CO2 from the atmosphere.
It is important to note that these percentages can vary slightly depending on the data source and the specific methodology used for calculations.
However, the general consensus among scientific organizations, such as the IPCC, supports these estimates.
Addressing emissions from these major sectors is crucial for mitigating climate change and achieving global climate targets.
Calculating Carbon Footprint
Calculating one’s carbon footprint can be a complex task as it involves evaluating emissions from various sources. However, several online tools, apps, and calculators are available to simplify the process.
These calculators consider factors such as energy consumption, transportation habits, waste management, and lifestyle choices to estimate the emissions associated with an individual or entity.
By providing valuable insights, these calculators empower individuals to make informed decisions and prioritize areas for emission reduction.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
Reducing our carbon footprint requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses both personal and collective actions. Here are some effective strategies:
- Energy Efficiency: Opt for energy-efficient appliances, LED lighting, and insulation improvements. Switch to renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power.
- Sustainable Transportation: Choose public transportation, carpooling, biking, or walking whenever possible. Transition to electric vehicles for a greener commute.
- Waste Management: Practice recycling, composting, and proper waste disposal. Reduce packaging waste and opt for reusable products.
- Responsible Consumption: Buy locally produced and seasonal goods to minimize transportation emissions. Reduce meat consumption and incorporate more plant-based foods into your diet.
- Conscious Travel: Offset the carbon emissions from air travel by supporting verified carbon offset projects. Consider exploring local destinations or eco-friendly travel options.
- Reforestation and Conservation: Support initiatives focused on reforestation and habitat preservation. Plant trees and participate in community-based conservation efforts.
As individuals, we hold the power to make choices that reduce our footprint and contribute to a sustainable future. By adopting energy-efficient practices, making conscious consumption decisions, and embracing eco-friendly transportation options, we can take significant steps towards mitigating climate instability.
It is essential for governments, organizations, and communities to collaborate and implement policies that support and encourage carbon footprint reduction. Let us take responsibility for our actions and leave a positive impact on the environment for generations to come.







