The 7 Plastic Recycling Numbers and Meanings
- 1. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) – Most easily recyclable
- 2. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) – Most easily recyclable
- 3. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
- 4. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
- 5. PP (Polypropylene)
- 6. PS (Polystyrene)
- 7. Other
In today’s world, plastic bottles have become an everyday commodity in our lives. From water bottles to soda bottles, plastic bottles have become a part of our routine.
However, with the excessive use of plastic bottles, the need for recycling has become increasingly important. Recycling some plastic bottles not only reduces waste but also helps conserve natural resources, energy, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The Plastic Recycling Numbers 1 to 7 Found Inside the Recycling Symbols
The plastic recycling numbers 1 to 7 found inside the recycling symbols on plastic products indicate the type of plastic that was used to make the product.
Here is a breakdown of the plastic recycling numbers meanings for each number:
1. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) – Most easily recyclable
This plastic is commonly used for water and soda bottles, food packaging, and containers. It is easily recyclable and can be repurposed into carpet, clothing, and other consumer products.
2. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) – Most easily recyclable
This plastic is commonly used for milk jugs, detergent bottles, and other household items. It is easily recyclable and can be repurposed into plastic lumber, toys, and other consumer products.
3. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
This plastic is commonly used for piping, vinyl flooring, and some food packaging. It is not easily recyclable and is often not accepted in recycling programs.
4. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
This plastic is commonly used for plastic bags, shrink wrap, and some plastic containers. It is recyclable but is often not accepted in curbside recycling programs.
5. PP (Polypropylene)
This plastic is commonly used for yogurt cups, margarine tubs, and some food packaging. It can be recycled and can be repurposed into automotive parts, furniture, and other consumer products
6. PS (Polystyrene)
This plastic is commonly used for foam cups, takeout containers, and packaging materials. It is not easily recyclable and is often not accepted in curbside recycling programs.
7. Other
This category includes plastics made from materials other than the six listed above, such as polycarbonate and bioplastics. The recyclability of these materials varies and may not be accepted in all recycling programs.
Not all plastic bottles are created equal, and not all of them can be recycled.
Understanding what type of plastic bottles can and cannot be recycled is crucial in ensuring that we are effectively reducing waste and conserving natural resources.
The most commonly recycled plastic bottles are made of PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and are easily recognizable by the recycling symbol with a number 1 inside it. These are commonly used for:
- Water bottles
- Soda bottles
- Salad dressing bottles
- Cooking oil bottles
It’s important to note that just because a plastic product has a recycling symbol with a number on it doesn’t necessarily mean it is recyclable in your area.
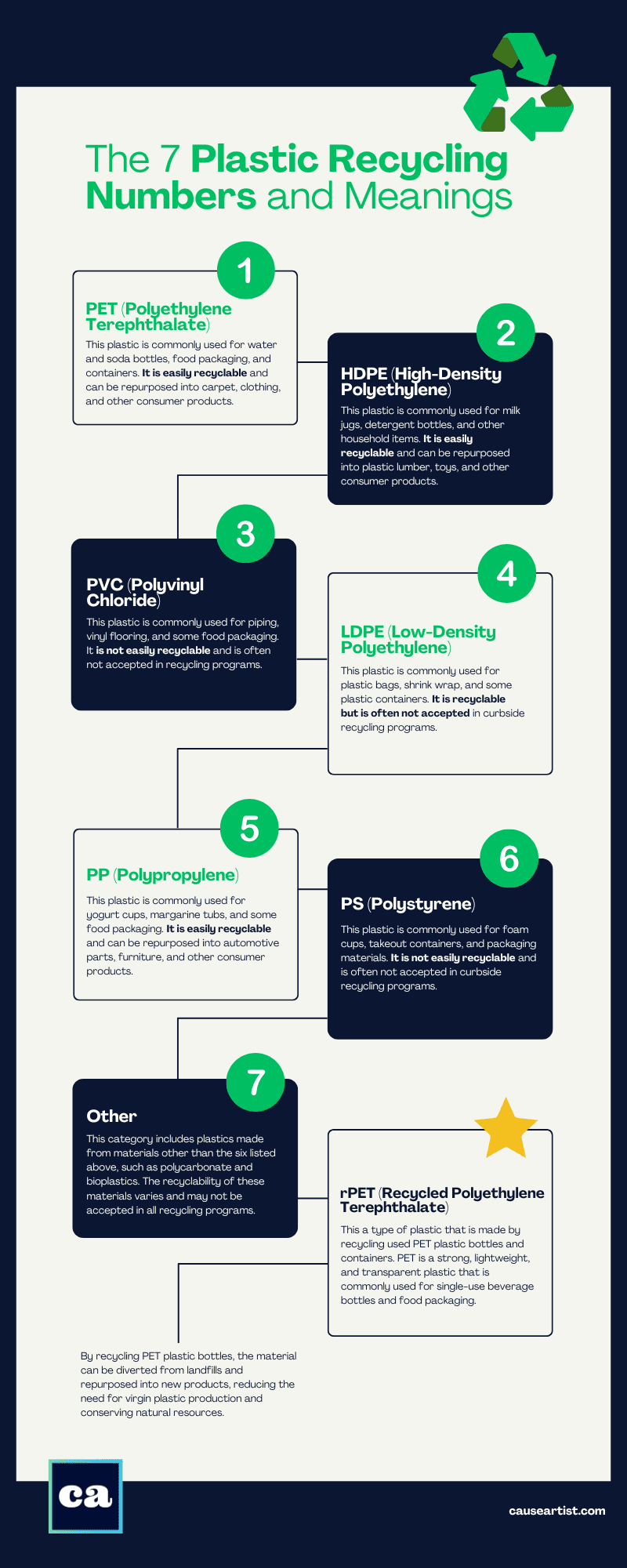
rPET Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate
Not mentioned above, but perhaps the most important to know about and look for is rPET, or recycled polyethylene terephthalate.
This a type of plastic that is made by recycling used PET plastic bottles and containers. PET is a strong, lightweight, and transparent plastic that is commonly used for single-use beverage bottles and food packaging.
By recycling PET plastic bottles, the material can be diverted from landfills and repurposed into new products, reducing the need for virgin plastic production and conserving natural resources.
The process of creating rPET begins with the collection and sorting of used PET bottles. The bottles are then washed and shredded into small flakes or pellets.
These flakes are then melted down and extruded into new plastic products, such as new bottles, containers, and even clothing.
rPET is a sustainable alternative to virgin PET plastic, as it uses less energy and natural resources to produce.
Additionally, recycling PET plastic bottles helps to reduce the amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills and in the environment.
Many companies are now using rPET in their packaging and products, as consumers increasingly demand more sustainable and environmentally friendly options.
It’s important to note that while rPET is a more sustainable option than virgin PET plastic, it is still a single-use material that contributes to waste and pollution.
To truly reduce our impact on the environment, we need to reduce our consumption of single-use plastics and transition to more sustainable alternatives, such as reusable containers and packaging.
The Benefits of Recycling Plastic Bottles
- Conservation of Natural Resources One of the most significant benefits of recycling plastic bottles is the conservation of natural resources. By recycling plastic bottles, the amount of virgin plastic used is reduced. Virgin plastic is made from petroleum, which is a non-renewable resource. By using recycled plastic, we reduce the demand for virgin plastic, thereby conserving natural resources.
- Reduction in Energy Consumption Recycling plastic bottles requires less energy compared to producing new plastic bottles. The process of producing new plastic bottles involves extracting petroleum, transporting it to the refinery, refining it, and then transporting it to the plastic manufacturing plant. On the other hand, recycling plastic bottles involves collecting, sorting, and cleaning them before melting and reforming them into new products. Recycling plastic bottles requires less energy than producing new ones, which reduces greenhouse gas emissions and conserves energy.
- Reducing Landfill Waste Plastic bottles are a significant contributor to landfill waste. When plastic bottles are disposed of in landfills, they take hundreds of years to decompose. As they decompose, they release harmful chemicals into the soil, which can contaminate groundwater. Recycling plastic bottles helps reduce the amount of waste that goes to landfills, thereby reducing the negative impact on the environment.
- Lowering Greenhouse Gas Emissions Producing new plastic bottles requires a significant amount of energy, which is generated by burning fossil fuels. Burning fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, which contribute to climate change. Recycling plastic bottles reduces the demand for new plastic bottles, which in turn reduces the amount of energy required to produce them, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
How to Recycle Plastic Bottles
- Know What Can be Recycled Before you start recycling plastic bottles, it’s essential to know what can be recycled. Not all plastic bottles are recyclable, and it’s important to know what can and cannot be recycled. Plastic bottles made from PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) can be recycled. These bottles are commonly used for water bottles, soda bottles, and salad dressing bottles. However, plastic bottles made from other materials such as PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) cannot be recycled.
- Clean and Sort the Bottles Before recycling plastic bottles, it’s important to clean and sort them. Empty the bottles and rinse them with water to remove any leftover contents. Once the bottles are clean, sort them according to their color. Clear plastic bottles are usually made from pure PET, while colored bottles may have other additives that make them harder to recycle.
- Find a Recycling Center Once you have cleaned and sorted your plastic bottles, the next step is to find a recycling center. Most cities have a recycling program that collects plastic bottles, but if your city does not have one, you can find a local recycling center. Many grocery stores and retail chains also have recycling programs for plastic bottles.
- Consider Reusing Before recycling plastic bottles, consider reusing them. Plastic bottles can be reused for various purposes such as storing water, juice, or other liquids. Reusing plastic bottles not only reduces waste but also reduces the need for new plastic bottles.








